
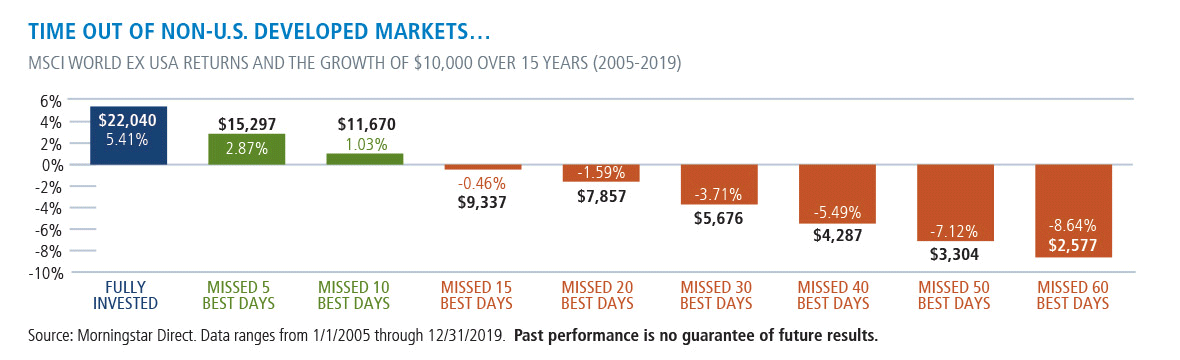
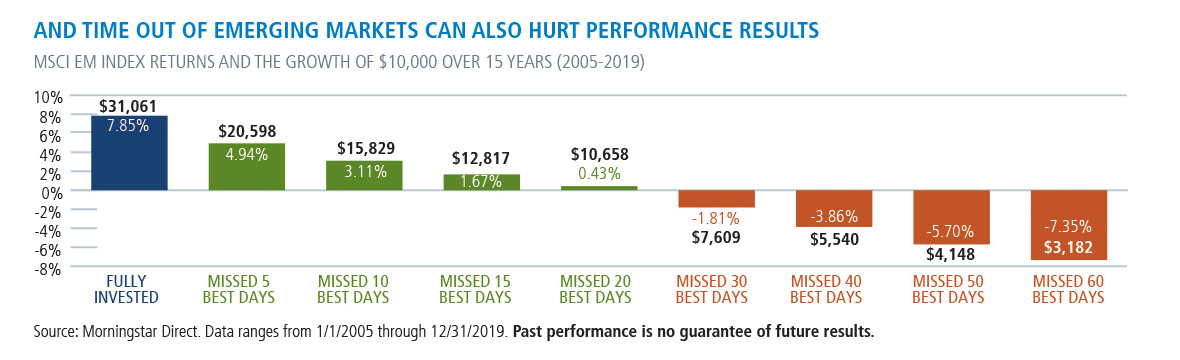
Staying Invested In International Markets Makes Good Sense, Too
What's true of investing in U.S. markets also applies to those who invest for the long term in non-U.S. markets. Efforts to time international markets can be costly, as well.
Before investing, carefully consider the fund’s investment objectives, risks, charges and expenses. Please see the prospectus and summary prospectus containing this and other information which can be obtained by calling 1-866-363-9219. Read it carefully before investing.
Opinions and estimates offered constitute our judgment and are subject to change without notice, as are statements of financial market trends, which are based on current market conditions. We believe the information provided here is reliable, but do not warrant its accuracy or completeness. This material is not intended as an offer or solicitation for the purchase or sale of any financial instrument. The views and strategies described may not be suitable for all investors. This material has been prepared for informational purposes only, and is not intended to provide, and should not be relied on for, accounting, legal or tax advice. References to future returns are not promises or even estimates of actual returns a client portfolio may achieve. Any forecasts contained herein are for illustrative purposes only and are not to be relied upon as advice or interpreted as a recommendation.
Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
Indexes are unmanaged, not available for direct investment and do not include fees and expenses.
The S&P 500 Index is considered generally representative of the U.S. equity market.
The MSCI Emerging Markets Index is a measure of the performance of emerging market equities.
The MSCI World Index is a market capitalization weighted index composed of companies representative of the market structure of developed market countries in North America, Europe, and Asia/ Pacific region.
Foreign Securities Risk — Risks associated with investing in foreign securities include fluctuations in the exchange rates of foreign currencies that may affect the U.S. dollar value of a security, the possibility of substantial price volatility as a result of political and economic instability in the foreign country, less public information about issuers of securities, different securities regulation, different accounting, auditing and financial reporting standards and less liquidity than in U.S. markets.
Emerging Markets Risk — Emerging market countries may have relatively unstable governments and economies based on only a few industries, which may cause greater instability. The value of emerging market securities will likely be particularly sensitive to changes in the economies of such countries. These countries are also more likely to experience higher levels of inflation, deflation or currency devaluations, which could hurt their economies and securities markets.
Cookies
This website uses cookies. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies. Learn more about our cookie usage.

